The Future of Medicine: XR Technologies Revolutionize Education, Practice, and Patient Care.
In our key areas of focus, we want to introduce you to the diverse applications of extended reality (XR) in medicine: education, training and professional development, medical application, and use for patients. Here, you will get a comprehensive overview of the innovative XR solutions that contribute significantly to improving medical education, the clinical routine, and the well-being of patients. Learn more about the role of virtual and extended reality in expanding medical knowledge and the skills of professionals, revolutionizing medical care, and focusing on the needs of the patients. Be inspired by the various application possibilities and discover how these technologies are sustainably transforming the healthcare sector.
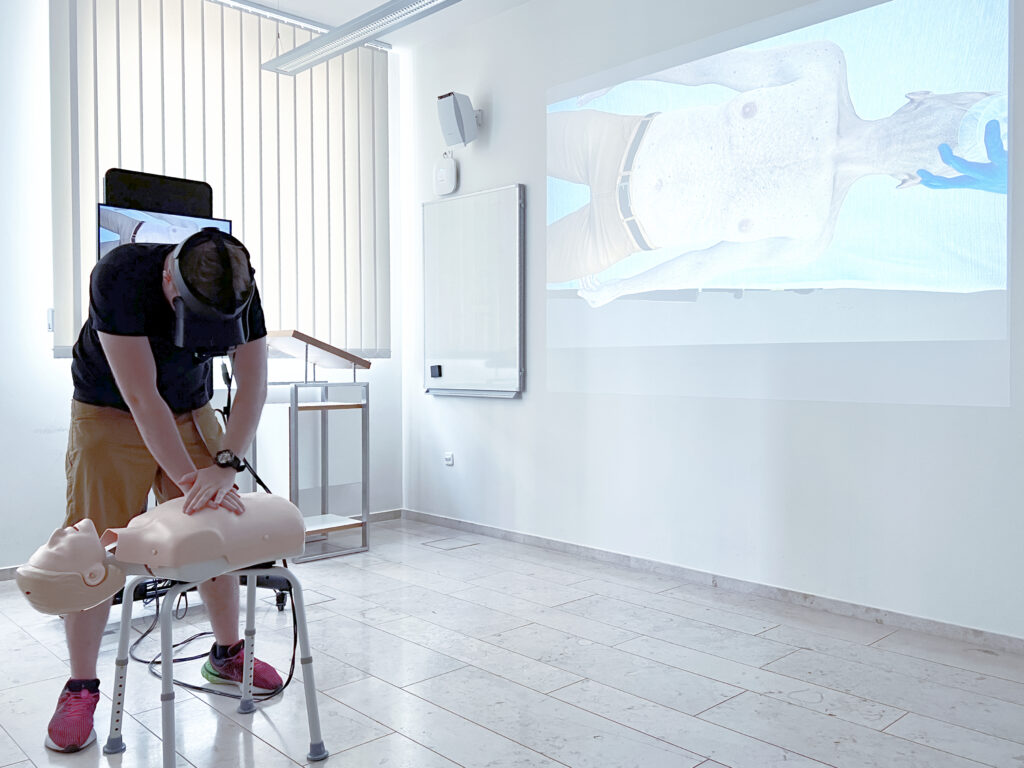

Education, training and professional development
Imparting medical knowledge and training procedural routines and behaviors is a crucial component in education, training, and professional development. In this focus area, the ZvRM deals with innovative XR solutions specifically designed for conveying medical knowledge and training medical procedures and behaviors. For instance, VR simulations can assist in surgical and anesthesia training, enhancing skills in a realistic environment. Training with VR technology allows practitioners to practice complex procedures and make vital decisions without exposing patients to any risk. Another application is AR-supported learning modules that enablestudents and aspiring doctors to explore and understand intricate anatomical structures by viewing interactive 3D models on a tablet or through an AR headset.
Medical Application
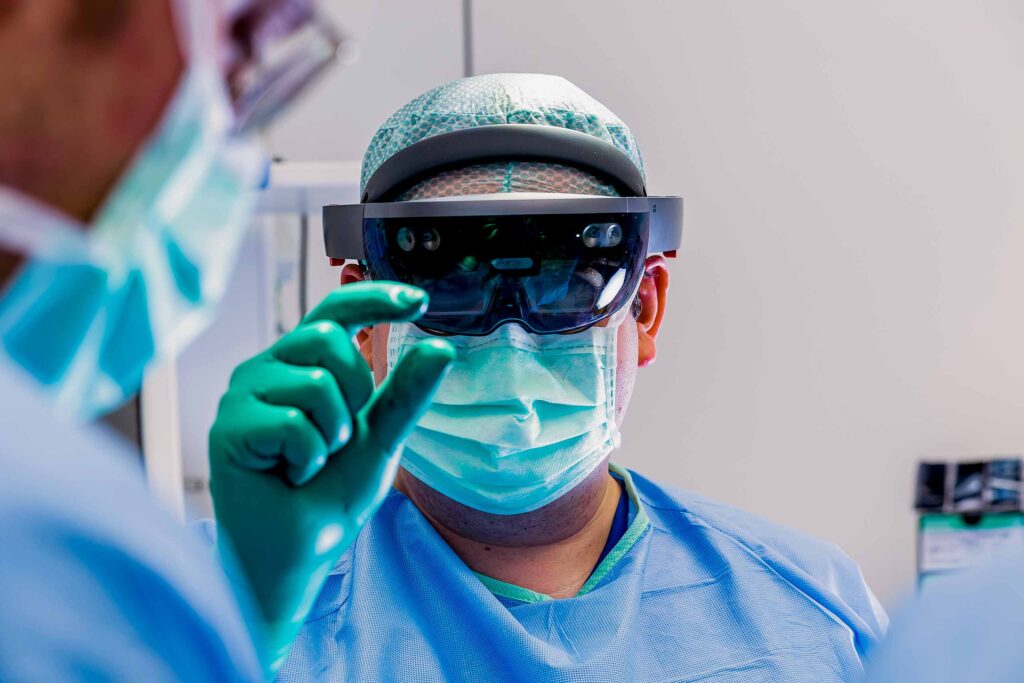
The “Medical Application” focus includes XR solutions specifically developed for daily use in medical practice. From diagnostics to therapy, these solutions offer a wide range of applications that contribute to the improvement of medical care. The spectrum of applications ranges from communication in the doctor-patient relationship, assistance in diagnosis, to surgical interventions. For instance, the control of surgical robots can be trained in virtual reality. In immediate surgical situations, AR-based assistance systems are also used for the visualization and marking of surgery-relevant data during surgical procedures. This way, preoperatively created radiological images can be projected intraoperatively onto the patient using AR systems and used as a roadmap. Additionally, XR solutions can also be employed in physiotherapy and sports therapy to support physical and mental recovery of patients.
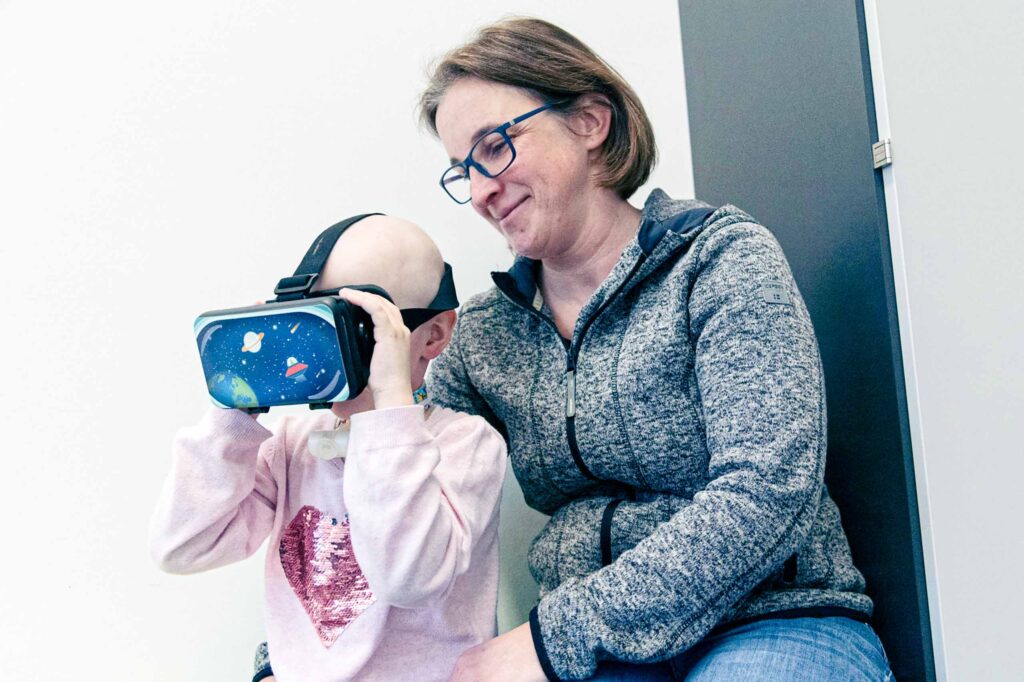

Patient-Centered Application
This focus area centers on XR solutions aimed at enhancing the well-being of patients before, during, and after their stay in the hospital. They provide opportunities to convey knowledge and educate patients about their illness, therapy, and hospital procedures. Moreover, they offer entertainment options and promote physical and emotional well-being of the patients and their peers.